Curious about US accounting? This guide explains GAAP standards, career opportunities for Indian professionals, and key compliance aspects
Key Takeaways
- U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) ensure consistency and transparency in financial reporting, influenced increasingly by International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Indian accounting professionals can capitalize on job opportunities in the U.S. with a CPA designation, leveraging networks and programs such as Miles US Pathway for extended work permits.
- Compliance with GAAP is essential for public companies in the U.S. to maintain stakeholder trust, requiring rigorous internal controls to prevent errors and ensure accurate financial statements.
Overview of US Accounting Standards
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) are the cornerstone of financial reporting in the United States. These accounting principles ensure that financial statements are consistent, comparable, and transparent, which is crucial for stakeholders making informed decisions. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the body responsible for issuing and maintaining these standards, ensuring that they evolve to meet the changing needs of the financial landscape.
Recently, international standards like IFRS have increasingly influenced the US. Converging US GAAP with IFRS aims to harmonize accounting practices globally, facilitating smoother cross-border financial activities. This trend underscores the importance of understanding both US GAAP and international standards for professionals in the field.
Opportunities for Indian Professionals
The US economy presents a plethora of opportunities for Indian accounting professionals, ranging from public accountants to management and government accountants. The average annual salary for accountants and auditors in the US is over $70,000, with entry-level positions starting at around $50,000 to $60,000. This makes the US an attractive destination for Indian professionals looking to advance their careers.
A Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation significantly boosts career prospects, opening doors to high-level positions in major firms like Deloitte, KPMG, and EY. Leveraging networking, job portals, and recruitment agencies helps Indian professionals secure positions in the US.
Programs like the Miles US Pathway also offer extended work permits, facilitating a 3-year work opportunity post-education.
Importance of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
GAAP is paramount in ensuring the completeness, consistency, and comparability of financial statements. These principles are designed to provide accurate and transparent financial information, which is essential for stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and regulatory agencies. Adhering to GAAP bolsters an organization’s credibility and enables stakeholders to make informed decisions based on reliable data.
Historical financial crises significantly influenced GAAP’s evolution, highlighting the need for standardized and accurate financial reporting. This framework not only enhances comparability across companies but also builds trust in the financial markets by providing a dependable standard for financial reporting.
Moreover, GAAP compliance ensures that financial statements are prepared consistently across reporting periods, enhancing their utility for comparative analysis. This consistency is crucial for stakeholders who rely on these statements to assess the financial health and performance of organizations.
Key Principles of US GAAP
Understanding the key principles of US GAAP is essential for ensuring accurate financial reporting. The revenue recognition principle dictates that income should be recorded when it is earned, not necessarily when cash is received. This principle ensures that revenue is matched with the period it is generated, providing a more accurate financial picture.
Another critical principle is the matching principle, which requires that expenses be recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate. This alignment ensures that financial statements reflect the true profitability of operations.
Additionally, the full disclosure principle mandates that all significant information must be included in financial reports, ensuring transparency for stakeholders. This is often achieved through detailed notes accompanying the financial statements, providing context and additional detail about the reported figures.
Compliance With US GAAP
Compliance with US GAAP is mandatory for publicly traded companies in the US, ensuring a standardized approach to financial reporting. These companies must submit their financial statements to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), adhering to GAAP to maintain their stock exchange listings. This requirement underscores the importance of following GAAP rules for transparency and accuracy in financial reporting.
However, despite these stringent rules, financial statements can still contain errors due to potential manipulation. The SEC has increased its scrutiny of non-GAAP measures to prevent misleading investors. GAAP compliance requires rigorous internal controls and regular audits to detect and correct discrepancies, maintaining the integrity of financial reporting.
Common Pitfalls
Common pitfalls in GAAP compliance often revolve around revenue recognition and expense matching. Companies may fail to recognize revenue appropriately, leading to financial statements that misrepresent the company’s financial position. Avoiding these errors requires implementing clear policies and procedures for recording income, ensuring recognition in the correct accounting period.
Another prevalent issue is failing to match expenses with related revenues, which can distort profit assessments and cost evaluations. Regular training and updates for accounting staff on GAAP compliance and assistance significantly reduce the chances of errors.
Additionally, companies often overlook the full disclosure principle, resulting in insufficient information for stakeholders. Ensuring comprehensive disclosures and detailed notes in financial reports is vital for maintaining transparency and stakeholder trust.
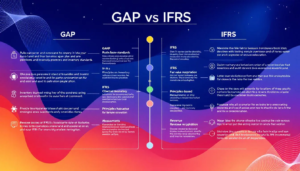
Differences Between GAAP and IFRS
The differences between GAAP and IFRS are significant, impacting how financial statements are prepared and presented. One notable difference is in inventory valuation:
- GAAP allows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) method.
- IFRS prohibits the LIFO method.
- Both frameworks permit the First In, First Out (FIFO) and weighted-average methods.
The allowance of LIFO under GAAP can lead to substantial differences in reported inventory values.
Another key difference lies in the treatment of inventory write-downs. IFRS allows the reversal of inventory write-downs if the market value increases, a practice not permitted under GAAP. Furthermore, while GAAP is generally rules-oriented, IFRS adopts a more principles-based approach, providing broader guidelines that require professional judgment.
Asset revaluation is another area where GAAP and IFRS diverge. Under IFRS, companies can revalue assets to fair value, whereas GAAP restricts this practice primarily to marketable securities. Understanding these differences is crucial for professionals dealing with international accounting standards, as they impact financial statement comparability and interpretation.
Role of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in Accounting
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) plays a pivotal role in enforcing tax laws and ensuring compliance with federal tax regulations in the US. The IRS collects various forms of taxes, including income and estate taxes, and conducts audits to verify taxpayer compliance. These audits are either randomly selected or targeted at returns with discrepancies or unusual deductions.
In 2024, the IRS processed over 163 million individual tax returns, underscoring its central role in the accounting practices associated with income tax. The IRS’s enforcement activities and regulatory oversight significantly impact how accounting practices are conducted, ensuring that organizations adhere to tax laws and regulations.
Understanding Taxation in the US
Taxation in the US is a complex system that includes both federal and state taxes. Individuals face a maximum personal income tax rate of 37%, while capital gains are taxed at a maximum rate of 20%. The standard deduction amount for 2024 is $14,600 for single filers, $29,200 for married couples filing jointly, and individual tax rates for heads of households are $21,900.
Itemized deductions may include expenses such as charitable contributions, mortgage interest, and significant medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of adjusted gross income. Understanding these deductions is crucial for taxpayers to minimize their taxable income and reduce their overall tax burden.
Corporations face a federal income tax rate of 21%, with state corporate income taxes ranging from 1% to 12%. There is no inheritance tax in the US, but estates may be subject to a federal estate tax with a top rate of 40%. These rates and regulations highlight the importance of understanding the US taxation system for both individuals and organizations.
Tax Deductions and Credits
Tax deductions and credits are vital tools for reducing taxable income and the amount owed in taxes. In the US, individuals and corporations are taxed based on their net taxable income, which is calculated by applying a tax rate to the total income after allowable deductions for tax purposes. This system allows taxpayers to choose between taking a standard deduction or itemizing their deductions, depending on which method provides a greater tax benefit. Understanding tax law is essential for maximizing these benefits and to claim them effectively.
Various expenses, including alimony, business expenses, and certain educational costs, can be deducted from income, potentially lowering overall taxable income. Tax credits, on the other hand, directly reduce the amount owed in taxes, and certain credits are refundable, meaning they can result in a refund even if no taxes are owed.
Taxpayers must file annual tax returns by April 15th to reconcile the taxes owed with amounts already paid through payroll deductions or estimated payments. The US taxation system also allows for estimated tax payments for both corporate and personal income taxes, typically due on a quarterly basis.
Financial Statements Under US GAAP
Financial statements are crucial for depicting a company’s financial health and performance. Under US GAAP, publicly traded companies must follow specific rules and file their financial statements regularly with the SEC. These statements include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, each serving a unique purpose.
The balance sheet reflects a company’s financial position at a specific date in time, detailing financial assets, liabilities, and equity. The income statement, also known as the statement of earnings, provides a summary of revenues and expenses over a period, showing the entity’s profitability.
The cash flow statement provides insights into cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities during a specific period. Together, these statements provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial status.
Impact of US GAAP on Investors
US GAAP plays a pivotal role in the investment landscape by ensuring that financial statements are consistently complete and comparable. This consistency aids investors in analyzing various companies and making informed financial decisions. By adhering to GAAP, companies provide a reliable basis for investors to evaluate their financial health and performance.
The transparency required by GAAP helps maintain investor trust in financial markets, which in turn reduces transaction costs and fosters a more stable investment environment. Investors rely on GAAP-compliant financial statements to compare financial data across companies within the same industry, facilitating better investment choices.
Financial statements that do not comply with GAAP can mislead investors, making it difficult to accurately compare the financial performance of different companies. This can lead to poor investment decisions and could potentially undermine trust in the financial markets. Therefore, GAAP compliance is essential for maintaining the integrity and reliability of financial information.
Non-GAAP Measures
Non-GAAP measures are figures presented without adhering to GAAP guidelines, and they are typically identified specifically as non-GAAP. Companies often use these measures to capture specific operational nuances that are not reflected by GAAP, providing an alternative view of performance.
However, while non-GAAP measures can offer valuable insights, they also present risks. They can potentially mislead investors if not properly contextualized. Many companies report figures that deviate from GAAP, with 77% of S&P 500 companies reporting adjusted earnings and similar percentages using other non-GAAP metrics like adjusted EPS and EBITDA.
This prevalence underscores the need for careful interpretation by investors to avoid confusion and ensure a true understanding of businesses and access to obtain a company’s financial health through research to determine the best investment strategies.
Career Opportunities for Indians in US Accounting and Taxation
The demand for accounting professionals in the US is projected to grow, providing numerous opportunities for Indian professionals to enter the field. Many firms in the US actively seek accounting professionals with international qualifications, particularly those from India, due to the diverse skills they bring. Key employers in the US accounting sector include major firms like Deloitte, KPMG, and EY, which often look for candidates who qualify with strong backgrounds in GAAP and IFRS.
Indian accountants can find roles in various sectors, including corporate finance, international taxation, and auditing, which are critical for business compliance. Networking and obtaining relevant certifications, such as the CPA, can significantly enhance career prospects. As the integration of international standards continues, professionals with knowledge of both GAAP and IFRS are particularly valuable.
Resources for Learning US Accounting
Mastering US accounting principles is enhanced through various valuable resources, including eBooks, online courses, and professional organizations. The Oxford Home Study Centre offers a free Certificate in Accounting and Finance course that covers essential accounting concepts. LinkedIn Learning provides a free course on Accounting Ethics, focusing on professional accountability and internal controls. This course encourages learners to act with integrity in their accounting practices.
The Accounting Workflow Academy includes a course on Setting Up Accounting Processes to enhance workflow efficiency, and the University of Illinois offers a Managerial Accounting course that aids accountants in corporate financial decision-making. For those interested in forensic accounting, free courses on Forensic Accounting and Fraud Examination are available, equipping accountants with skills to detect fraud.
The University of Pennsylvania offers several accounting courses that provide a comprehensive foundation for anyone looking to excel in US accounting:
- Accounting Analytics, which teaches ratio analysis and forecasting to bolster financial understanding.
- Accounting for Decision-Making, addressing unique accounting principles relevant to specific sectors.
- Accounting for the Charity Sector, focusing on accounting principles specific to the charity sector.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding US accounting and taxation is crucial for Indian professionals seeking to advance their careers in the US. The adherence to Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) ensures the reliability and transparency of financial statements, which is fundamental for making informed business decisions. The growing influence of international standards like IFRS further emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of these principles.
Career opportunities in the US are abundant for Indian professionals, particularly those with qualifications like the CPA and a strong grasp of GAAP and IFRS. The integration of technology and data analytics in accounting practices opens new avenues for growth and innovation. As you embark on your journey in US accounting and taxation, leverage the resources and opportunities available to build a successful and fulfilling career.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main objectives of GAAP?
The main objectives of GAAP are to ensure the completeness, consistency, and comparability of financial statements, which in turn provides accurate and transparent financial information for stakeholders. This framework is essential for maintaining trust and integrity in financial reporting.
How does obtaining a CPA designation benefit Indian accountants in the US?
Obtaining a CPA designation greatly enhances career opportunities for Indian accountants in the US, facilitating access to high-level positions within prestigious firms and improving competitiveness in the job market. This credential is pivotal for career advancement and professional recognition.
What are some common pitfalls in GAAP compliance?
Common pitfalls in GAAP compliance include errors in revenue recognition, improper matching of expenses with related revenues, and insufficient disclosure of significant information. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement clear policies and provide regular training for staff.
How do GAAP and IFRS differ in terms of inventory valuation?
GAAP permits the Last In, First Out (LIFO) method for inventory valuation, whereas IFRS prohibits it, resulting in significant differences in reported inventory values. Both frameworks do allow FIFO and weighted-average methods, but the LIFO allowance under GAAP can skew financial comparisons.
What resources are available for learning US accounting principles?
A variety of resources are accessible for learning US accounting principles, including free courses from the Oxford Home Study Centre, LinkedIn Learning, and the University of Illinois. Specialized courses in areas such as forensic and managerial accounting are also available to further enhance your understanding.